MutSeqR: Open Standards for Error-Corrected Sequencing Analysis
Standardizing Error-Corrected Sequencing Data Analysis
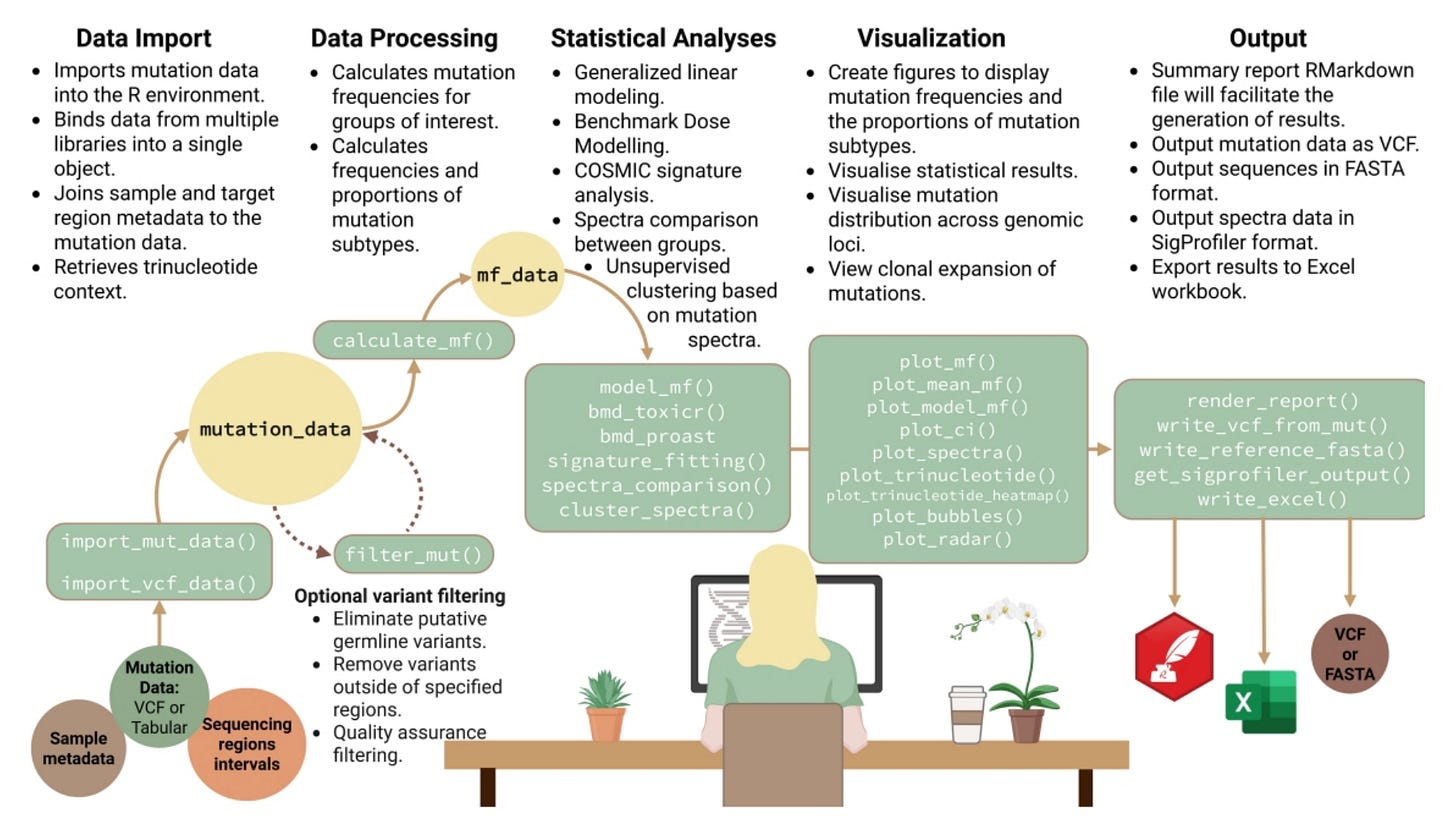
Figure 1 from MutSeqR publication showing an overview of the MutSeqR utilities.
At Fulcrum Genomics, we’ve always believed that open and reproducible methods are essential to advancing science. That’s why we’re proud to share that our own Clint Valentine co-authored a new publication in Bioinformatics Advances introducing MutSeqR. It’s an open-source R package designed to bring standardization to error-corrected sequencing (ECS) data analysis for genetic toxicology applications and beyond.
ECS has become a cornerstone technique in genetic toxicology, environmental health, and cancer research. By comparing multiple reads of both strands from the same DNA molecule, ECS can dramatically improve accuracy and detect ultra-rare mutations that traditional sequencing might miss in a sea of noise.
Despite its power, one major challenge has persisted: the lack of open and reproducible methods for analyzing ECS data for what genetic toxicology researchers and regulators care about. Different laboratories often use proprietary or custom-built pipelines, which make it difficult to compare results or reproduce findings.
MutSeqR addresses that challenge head-on.
What is MutSeqR?
MutSeqR was developed collaboratively by Health Canada, the University of Ottawa, and our team at Fulcrum Genomics. The goal was to create a shared, open framework for analyzing mutation data across ECS technologies like Duplex Sequencing (DS) and SMM-Seq.
Key features of MutSeqR:
Variant filtering and classification: Applies validated filters and identifies mutation types across ECS platforms
Mutation frequency and dose-response modeling: Quantifies how mutation rates change across experimental conditions
Benchmark dose (BMD) estimation: Implements statistical modeling consistent with regulatory methods for chemical risk assessment
Mutation spectrum and signature analysis: Characterizes mutation types and connects them to biological mechanisms
Built-in visualization tools: Generates reproducible plots for mutation frequency, spectra, and statistical comparisons
All analyses can be run in R (v3.4.0 or higher), and the code is openly available on GitHub.
Fulcrum Genomics’ Role
Our Ops Lead, Clint Valentine, contributed as a co-author on the study and helped establish many of the methods and software foundations that MutSeqR builds upon.
“This work reflects Fulcrum’s commitment to open and reproducible science,” said Valentine. “Our team has been developing tools for error-corrected sequencing for more than a decade, so it’s meaningful to see those methods evolve into frameworks that support regulatory applications.”
Matt Meier, of Health Canada and senior author on the paper, added: “For technologies like error-corrected sequencing to be used in a regulatory setting, we need open and transparent methods. Annette Dodge, first author on the publication, worked meticulously to build a tool that meets that need. It’s been rewarding to bring together experts from different disciplines to create something that serves the entire genetic toxicology community.”
This project continues a theme in our work at Fulcrum: helping scientists build confidence in their data through robust bioinformatics tools. Whether we’re consulting on experimental design, developing analysis pipelines, or contributing to open-source software, our goal is always the same: to help research teams make sense of complex genomic data with clarity and precision.
Why Standardization Matters for Genetic Toxicology
In toxicology and environmental genomics, reproducibility is essential for regulatory confidence. Small differences in variant calling or filtering parameters can lead to divergent conclusions about a chemical’s mutagenic risk.
MutSeqR brings consistency to these workflows by:
Supporting cross-platform comparability among ECS technologies
Offering transparent statistical models for mutation frequency and dose-response
Providing regulatory-aligned analysis tools for mutagenicity testing
Ensuring data reproducibility across labs and studies
MutSeqR’s benchmark dose modeling also aligns with methodologies already used by Health Canada, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), making it easier for results to be interpreted in a regulatory context.
Together, these tools make MutSeqR a valuable resource for researchers and regulators who need reliable, open-source methods for evaluating genetic safety data.
Looking Ahead: Open Science and Public Benefit
We see the publication and release of MutSeqR as part of a broader movement toward open and transparent genomics methods in genetic toxicology. As error-corrected sequencing continues to expand in research, industry, and government, tools like MutSeqR help bridge the gap between data generation, interpretation, and subsequent public health decision-making.
We’re excited about what comes next. Our open-source pipeline, fastquorum, already takes researchers from raw sequencing data to highly accurate error-corrected DNA sequences. MutSeqR now picks up from variant calls with variant filtering and annotation, dose response modeling, statistics, and visualization. But one automated piece is still missing: variant calling. We’d love to collaborate with others to develop this step or extend our existing tools toward an end-to-end open workflow for all the various flavors of error-corrected sequencing analysis. We want to see a solution with the same reproducible, regulatory-minded approach, that further helps researchers get the answers they need quickly and openly.
At Fulcrum Genomics, we remain committed to building open standards and collaborative methods that strengthen scientific integrity and transparency in genomics.
📖 Read the publication:
💻 Access the code: